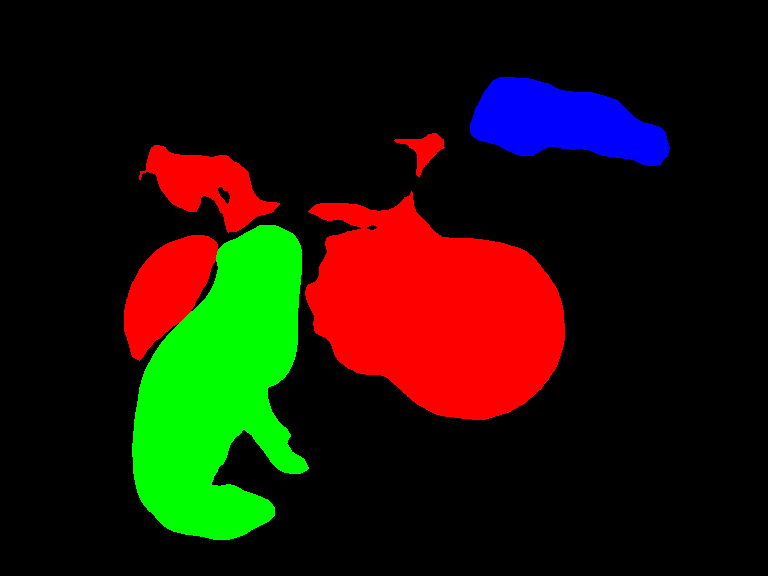
Semantic segmentation example¶
Semantic segmentation refers to the task of detecting objects of various classes at pixel level. It colors the pixels based on the objects detected in that space.
In this example, you learn how to implement inference code with Deep Java Library (DJL) to segment classes at instance level in an image.
The following is the semantic segmentation example source code:
Setup guide¶
Follow setup to configure your development environment.
Run semantic segmentation example¶
Input image file¶
You can find the image used in this example in project test resource folder: src/test/resources/segmentation.jpg

Build the project and run¶
cd examples
./gradlew run -Dmain=ai.djl.examples.inference.cv.SemanticSegmentation
This should produce the following output
[INFO ] - Segmentation result image has been saved in: build/output/semantic_instances.png
With the previous command, an output image with bounding box around all objects will be saved at: build/output/semantic_instances.png:

Run another semantic segmentation example¶
Input image file¶
You can find the image used in this example in project test resource folder: src/test/resources/dog_bike_car.jpg
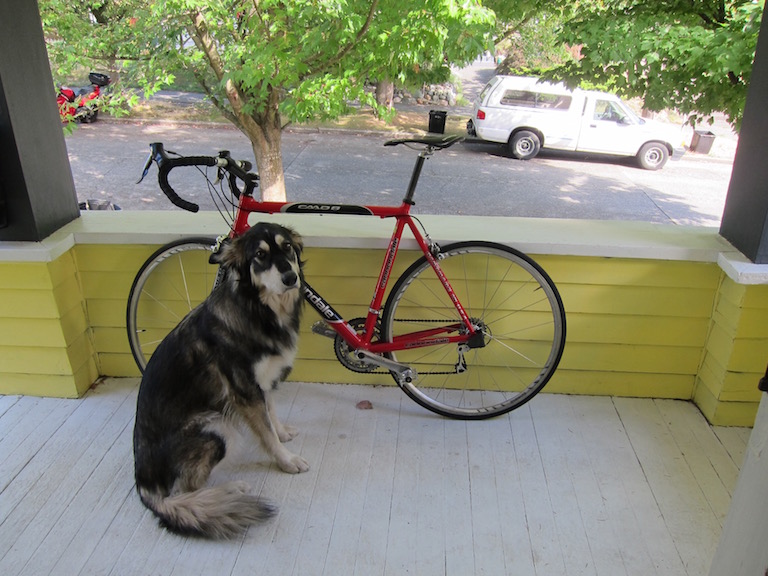

Edit project to run inference with new image¶
In the SemanticSegmentation.java file, find the predict() method. Change the imageFile path to look like this:
Path imageFile = Paths.get("src/test/resources/dog_bike_car.jpg");
Build the project and run¶
cd examples
./gradlew run -Dmain=ai.djl.examples.inference.cv.SemanticSegmentation
This should produce the following output
[INFO ] - Segmentation result image has been saved in: build/output/semantic_instances.png
With the previous command, an output image with bounding box around all objects will be saved at: build/output/semantic_instances.png: